Wireless Network: 3. Mobile Radio Propagation
Speed, Wavelength, Frequency
c = λ * f
- The lightspeed is constant. (3 * 10^8 m/s)
Types of Waves
- Space wave (upper Ionosphere)
- Sky wave
- Ground wave
Ground wave
- follows the contour of the earth
- can propagate over the visual horizon
- <= 2MHz
- AM radio
Skywave
- bounces between Ionosphere and the earth's surface
- 2MHz ~ 30MHz
Line-of-sight propagation
- no bounce, straight propagation
- for satellite communications and ground communications
- 30MHz ~
Signals
- analog / digital
- analog = continuous time, continuous values
- digital = discrete time, discrete values
- periodic signals
- is a sine wave, a model for signal
Sine wave
- is the fundamental periodic signal
- s(t) = A[i] sin(2πf[t]t + Φ[t])
- peak amplitude (A)
- frequency (f), period (T=1/f)
- phase (Φ)
Composite signal
- addition of sine waves
Square wave
infinite sum : { sin(f=1, A=1), sin(f=3, A=1/3), sin(f=5, A=1/5), ... }
Antennas
- radiation pattern: measurement of radiation
Isotropic radiator
- only in a theoretical model
- equal radiation in all directions
Simple dipoles
Antenna gain
- maximum power in the direction of the main lobe compared to the isotropic radiator
- G = 10 lg(P2/ P1) dB
- isotropic power (P1)
- diopole power (P2)
Directed and sectorized antennas
Signal Propagation
Signal Propagation Ranges
- Transmission range; communication possible, relatively low error rate
- Detection range; detection possible, no communication possible
- Interference range; may not be detected, may interfere other transmissions
Signal propagations are affected by
- fading
- shadowing
- reflection; at large obstacles
- refraction; density of medium
- scattering; at small obstacles
- diffraction; at edges
Radio propagation effects
- direct signal (Line-of-Sight)
Propagation model
Free-space
- received signal power at distance d
P = A G Pt / (4 π d^2)
- Pt : transmitting power
- A : effective area of antenna; λ^2/π
- G : antenna gain
Land
P = Gt Gr Pt / L
- Gr : receiver antenna gain
- Gt : transmitte antenna gain
- L =
Path Loss
Free-space
- proportional between d^2 ~ d^4
Lp = Pt / Pr = (4πd / λ)^2
Land
- Lp = A d^β
- A : constant
- d : distance between t ~ r
- β : constant in typical urban area
Fading
- attenuation of the transmitted signal power
- caused by interference from multiple copies of TX -> RX arriving at different times
- consequence : signal error
Small-scale fading; Fast fading
- due to movement, doppler effect, multipath propagation
- short-term fluctuation in amplitude caused by the local multipath
Large-scale fading; Slow fading
- due to shadowing
Shadowing
- raining, leaves, etc
Doppler Shift
Moving speed effect
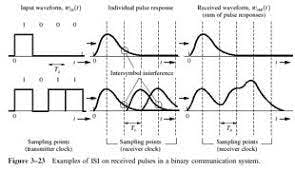
Delay spread
- measure of the multipath profile
- difference between the time of arrival of the earliest and the latest multipath component
Inter-symbol interference (ISI)